What is migraine?
With about 1 in every 5 Australians living with migraine – it’s a very common problem.2
One of the first things to understand about migraine is that it’s a complex condition. Despite being common, we don’t fully understand what causes migraine, and while there are ways to treat and even prevent migraine symptoms, migraine itself cannot be cured.
It’s not always easy to know if you’re experiencing a migraine attack as its severity and symptoms may vary, but you can usually narrow it down depending on the types of symptoms you have. So, if you’re experiencing throbbing or pulsating pain on one side of your head, nausea or vomiting, are sensitive to light or sounds, then you may be experiencing a migraine attack.
When you need relief from migraine attacks, either with or without aura, talk to your pharmacist about Imigran® Migraine. Imigran® Migraine is designed specifically for migraine relief and has been helping Australians find migraine relief for over 25 years3.
Imigran® Migraine is an effective treatment and when taken early, helps to stop the onset of migraine headache and other associated symptoms – so you can get on with the rest of your day.
If you’re finding it hard to manage your migraine or are getting frequent, constant headaches or migraine, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Who gets migraine?
What’s the difference between migraine and a headache?


Migraine is a neurological condition where you typically have moderate to severe headaches (usually on one side of the head).
A headache is only one symptom of migraine and it’s a particular type of headache – so, while migraine headaches can be severe, not all severe headaches are migraine headaches.
The main difference between a headache and migraine is that migraine can affect your whole body, and can be a distressing and debilitating experience.
What is a headache?

Headache pain can be felt differently depending on the cause.
A headache is the term used to describe pain felt in any part of your head.
Most people will have had a headache at some point in their life .
It’s one of the most common symptoms we get and can have many different triggers.
For example, the pain may be a throbbing, stabbing or shooting pain, be mild, moderate or severe, be on one or both sides of the head and last for a short time or go on for days.
Types of headache

Did you know, there are over 2004
different types of headaches?
Headaches are grouped into two different types:
Primary headaches – such as migraine headache, tension or stress headaches and cluster headaches, and are not linked to another medical condition
Secondary headaches – are symptoms of another health problem, such as sinus congestion or eye strain

Typically a one-sided throbbing pain
Can feel like pressure or a tightening band
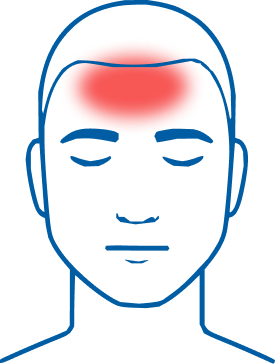
Usually mild or moderate pain
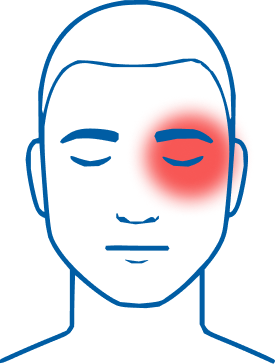
Extremely severe pain
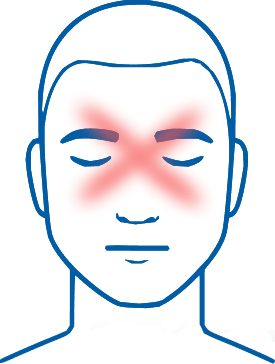
Usually mild to moderate pain
Common types of headaches
Often occurs with nausea or vomiting, or sensitivity to light or sounds
Frequency varies, can be 1-2 per month for some people or more than 15 days per month for others
Generally lasts from 4 hours to up to 3 days4
Generally not accompanied with other symptoms
Frequency and duration vary, but nearly everyone gets
them at some point
Attacks can last for hours to a few days
Can also occur with a red or watery eye, a runny or blocked nose and a drooping upper eyelid
Relatively uncommon but more likely to occur in men
Occurs frequently (once or twice daily) and often at night, but are usually short- lasting (up to 3 hours)
May occur with a blocked or congested nose and postnasal drip (mucus from your nose or sinuses dripping down the back of your throat)
Frequency varies but is often seasonal – particularly affects people with allergies
Generally lasts for hours if untreated
Often occurs with nausea or vomiting, or sensitivity to light or sounds
Frequency varies, can be 1-2 per month for some people or more than 15 days per month for others
Generally lasts from 4 hours to up to 3 days4
Generally not accompanied with other symptoms
Frequency and duration vary, but nearly everyone gets
them at some point
Attacks can last for hours to a few days
Can also occur with a red or watery eye, a runny or blocked nose and a drooping upper eyelid
Relatively uncommon but more likely to occur in men
Occurs frequently (once or twice daily) and often at night, but are usually short- lasting (up to 3 hours)
May occur with a blocked or congested nose and postnasal drip (mucus from your nose or sinuses dripping down the back of your throat)
Frequency varies but is often seasonal – particularly affects people with allergies
Generally lasts for hours if untreated
What is a Migraine headache?
Migraine may have many symptoms — one of which is a headache.
A migraine headache can last between 4 hours and several days4, with some people feeling unwell for a day or two before the migraine headache appears (although not all migraines have headaches).
Increased sensitivity to smell
Speech problems or difficulty concentrating
Tingling, pins and needles or numbness
2 Deloitte. Migraine in Australia Whitepaper.2018.
3 IMIGRAN sumatriptan 50mg. ARTG Public Summary (52261). Available at: https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ (accessed September 2023).
4 Steiner TJ, et al. Aids to management of headache disorders in primary care (2nd edition): on behalf of the European Headache Federation and Lifting The Burden: the Global Campaign against Headache. J Headache Pain. 2019;20(1):57.